Short-term solvency refers to the ability of a business to pay its short-term obligations when they become due. Short term obligations (also known as current liabilities) are the liabilities payable within a short period of time, usually one year. Companies may use days sales outstanding to better understand how long it takes for a company to collect payments after credit sales have been made. While the current ratio looks at the liquidity of the company overall, the days sales outstanding metric calculates liquidity specifically to how well a company collects outstanding accounts receivables. Simply take the current assets and divide them by the current liabilities.
How confident are you in your long term financial plan?
Today, we unravel the ‘Current Ratio,’ a key metric used to assess a company’s financial health. For example, in one industry, it may be more typical to extend credit to clients for 90 days or longer, while in another industry, short-term collections are more critical. Ironically, the industry that extends more credit actually may have a superficially stronger current ratio because its current assets would what’s the difference between salary vs wage employees be higher. In this example, the trend for Company B is negative, meaning the current ratio is decreasing over time. An analyst or investor seeing these numbers would need to investigate further to see what is causing the negative trend. It could be a sign that the company is taking on too much debt or that its cash balance is being depleted, either of which could be a solvency issue if the trend worsens.
How Do You Calculate the Current Ratio?
By examining multiple liquidity ratios, investors and analysts can gain a more complete understanding of a company’s short-term financial health. Other measures of liquidity and solvency that are similar to the current ratio might be more useful, depending on the situation. For instance, while the current ratio takes into account all of a company’s current assets and liabilities, it doesn’t account for customer and supplier credit terms, or operating cash flows.
What are Current Assets?
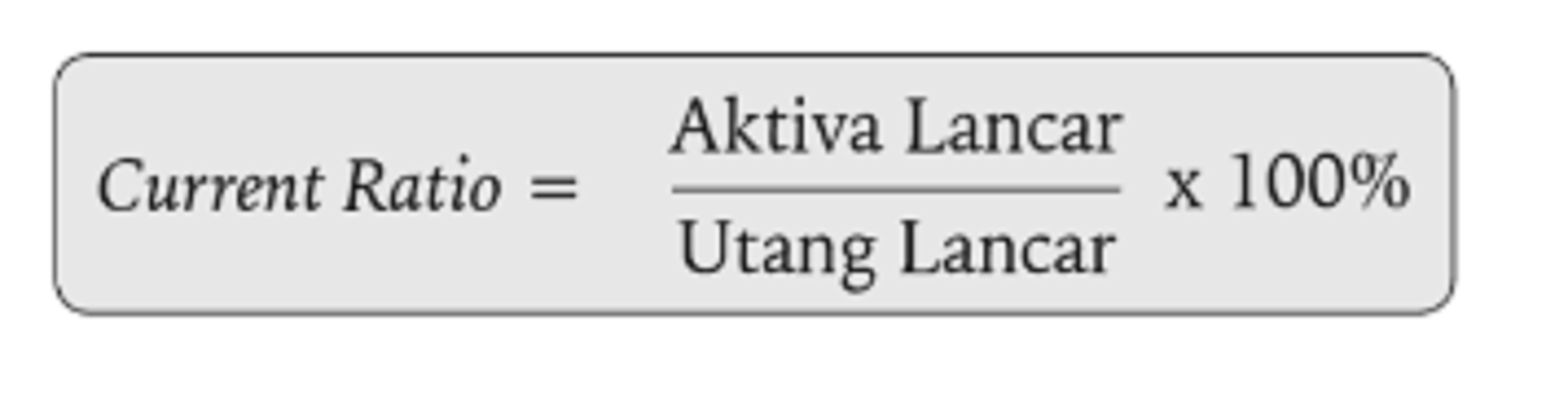
The current ratio is calculated simply by dividing current assets by current liabilities. The resulting number is the number of times the company could pay its current obligations with its current assets. The current ratio of 1.0x is right on the cusp of an acceptable value, since if the ratio dips below 1.0x, that means the company’s current assets cannot cover its current liabilities. The formula to calculate the current ratio divides a company’s current assets by its current liabilities. GAAP requires that companies separate current and long-term assets and liabilities on the balance sheet. This split allows investors and creditors to calculate important ratios like the current ratio.
- The denominator in the Current Ratio formula, current liabilities, includes all the company’s short-term obligations, i.e., those due within one year.
- The study samples a total of 40 listed firms from the Saudi stock market, using financial ratios to measure liquidity and profitability.
- This is important if you want to buy stock in a company that’s solvent and will remain that way for the long term.
Create a Free Account and Ask Any Financial Question
During times of economic growth, investors prefer lean companies with low current ratios and ask for dividends from companies with high current ratios. The Current Ratio provides valuable insights into a company’s liquidity. It’s particularly useful when assessing the short-term financial health of potential investment opportunities. This ratio, however, should not be viewed in isolation but rather as part of a holistic financial analysis. In the dynamic world of finance, it’s essential to navigate the complexities of financial ratios.

A ratio greater than 1 means that the company has sufficient current assets to pay off short-term liabilities. Current ratios are not always a good snapshot of company liquidity because they assume that all inventory and assets can be immediately converted to cash. This may not always be the case, especially during economic recessions. In such cases, acid-test ratios are used because they subtract inventory from asset calculations to calculate immediate liquidity.
The current ratio indicates a company’s ability to meet short-term debt obligations. The current ratio measures whether or not a firm has enough resources to pay its debts over the next 12 months. Potential creditors use this ratio in determining whether or not to make short-term loans. The current ratio can also give a sense of the efficiency of a company’s operating cycle or its ability to turn its product into cash.
Learn more about Bench, our mission, and the dedicated team behind your financial success. Get free guides, articles, tools and calculators to help you navigate the financial side of your business with ease. Learn the skills you need for a career in finance with Forage’s free accounting virtual experience programs. With that said, the required inputs can be calculated using the following formulas. Any estimates based on past performance do not a guarantee future performance, and prior to making any investment you should discuss your specific investment needs or seek advice from a qualified professional.
