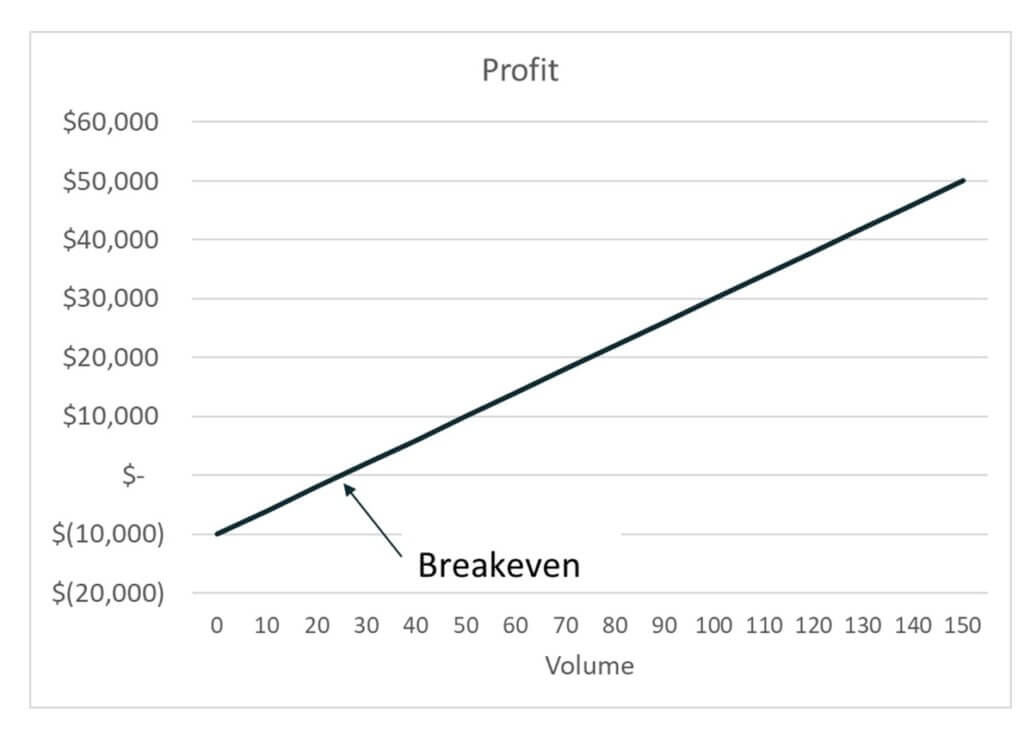
Volume, the second component, reflects the business’s level of activity or output. Understanding the relationship between volume and costs is crucial for effective financial planning and resource allocation. Here are the reasons why cost volume profit charts are the chic staple in the wardrobe of financial analysis. CVP Analysis can be used by managers to help them decide on pricing policies, output levels, what gamestop gains and losses mean for your taxes cost control strategies, and capital investments. It provides important information about how changes in costs and other factors will affect profitability as well as helps managers identify breakeven points for budgeting purposes. The owner wants to know the sales volume required in terms of both dollars ($) and the number of covers for the restaurant to break even considering its current expense structure.
Difference Between Cost Volume Profit Analysis And Break Even Analysis
As the number of units sold increases, so does operating income when fixed costs are within their relevant range and remain the same. This is shown in the following two income statements with sales of 1,200 and 1,400 units, respectively. Costs, the first component, represent the expenditures incurred by a business in its operations.
Identifying Contribution Margin Point in Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) Analysis
- The contribution margin ratio with the unit variable cost increase is 40%.
- There are some limitations related to CVP analysis that you need to keep in mind.
- Such decisions are usually based on past estimates and market research regarding the demand for products that are offered by the business.
- Cost categories that are typically included in a CVP analysis include fixed costs, variable costs, direct materials, direct labor, and overhead expenses.
Someone on our team will connect you with a financial professional in our network holding the correct designation and expertise. Our mission is to empower readers with the most factual and reliable financial information possible to help them make informed decisions for their individual needs. Our writing and editorial staff are a team of experts holding advanced financial designations and have written for most major financial media publications. Our work has been directly cited by organizations including Entrepreneur, Business Insider, Investopedia, Forbes, CNBC, and many others.
The Meat of the Matter: Finding the Break-Even Point in Units (or Sandwiches)
This provides a clear and easy visual representation of the amount you need to be selling to reach your target numbers. The sales price is the amount of money that a company charges for its products or services. In Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) analysis, the sales price is an important component used to calculate contribution margin, break-even point, and profitability. The contribution margin can be used to cover the fixed costs and generate a profit. In this example, the contribution margin of $10,000 can be used to cover the fixed costs of $10,000 and generates zero profit. CVP analysis is conducted to determine a revenue level required to achieve a specified profit.
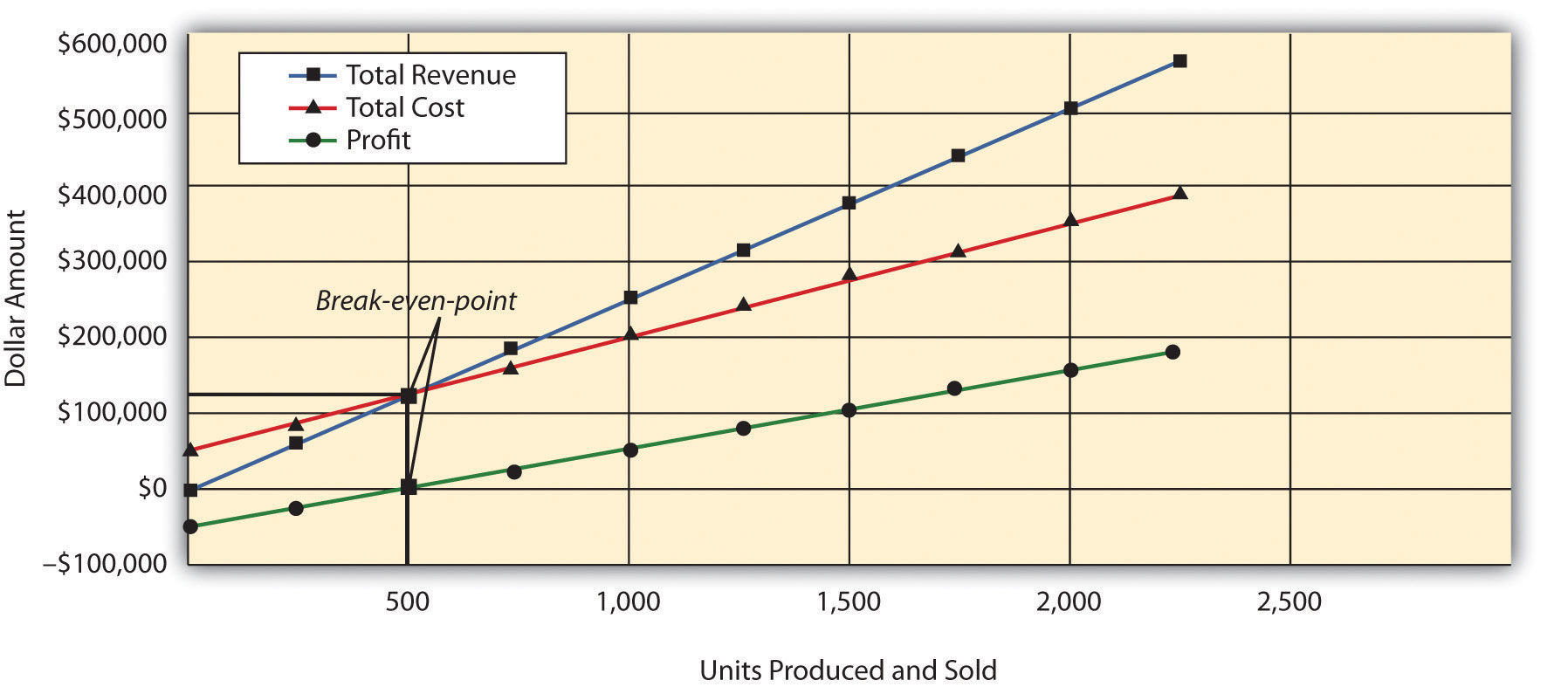
If the reality deviates too much from the initial assumptions, we might get a CVP analysis that provides us with conclusions that are not very beneficial for the company. The additional $5 per unit in unit selling price adds 7% to the contribution margin ratio. This visual line chart tells your story clearly outlining revenue, fixed costs, and total expenses, and the breakeven point. This is where total revenue and costs are equal, marking the point of neither profit nor loss. The break-even point is the ultimate fashion statement in financial equilibrium.
Limitations of Cost Volume Profit Analysis
The contribution margin indicates the amount ofmoney remaining after the company covers its variable costs. Thisremainder contributes to the coverage of fixed costs and to netincome. In Video Production’s income statement, the $ 48,000contribution margin covers the $ 40,000 fixed costs and leaves $8,000 in net income.
CVP analysis is only reliable if costs are fixed within a specified production level. All units produced are assumed to be sold, and all fixed costs must be stable in CVP analysis. Cost categories that are typically included in a CVP analysis include fixed costs, variable costs, direct materials, direct labor, and overhead expenses. These costs can be identified through an organization’s income statement or accounting records. Break-even analysis is concerned with determining the sales volume at which total revenue equals total costs so that profits are seen. Variable costs are costs that vary with the level of production or sales.
This video will give you an example of the why andhow to do a contribution margin income statement. CVP analysis helps management in finding out the relationship between cost and revenue to generate profit. The point where the total costs line crosses the total sales line represents the break-even point.
